General Information: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (23 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== General Information on Prokaryotic Elements == | |||
The "''General Information''" section of TnPedia offers a comprehensive overview of prokaryotic transposable elements (TEs), which are central to bacterial evolution and adaptation. These mobile genetic elements facilitate the acquisition and dissemination of genes responsible for antibiotic resistance, heavy metal tolerance, and virulence factors. | |||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
|+ | |+ | ||
|'''General Information on Prokaryotic Elements''' | |||
|- | |||
| width="680pt" | | | width="680pt" | | ||
;1. [[General Information/Overview|Overview]] | ;1. [[General Information/Overview|Overview]] | ||
| Line 13: | Line 16: | ||
;5. [[General Information/IS Identification|IS Identification, nomenclature and naming attribution]] | ;5. [[General Information/IS Identification|IS Identification, nomenclature and naming attribution]] | ||
;6. [[General Information/IS Distribution|IS Distribution]] | ;6. [[General Information/IS Distribution|IS Distribution]] | ||
| Line 52: | Line 52: | ||
;23. [[General Information/The casposases|The Casposases]] | ;23. [[General Information/The casposases|The Casposases]] | ||
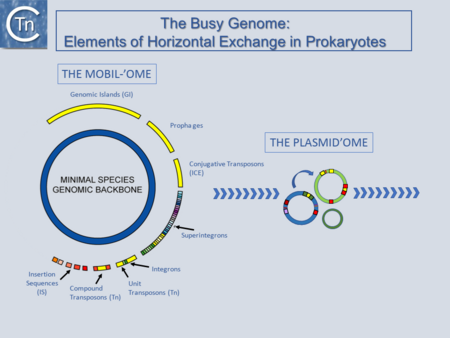
|} | |}[[Image:fig1.png|thumb|450x450px|[[General Information/Overview|'''Fig.1.1. The Busy Genome:''']] Elements of Horizontal Exchange. The genome backbone, which includes housekeeping genes, is shown as the inner circle (blue). The "mobilome" is shown in the outer circle. This includes a number of different types of MGE both intercellular (some genomic islands, prophages, and conjugative transposons) and intracellular (Insertion sequences, compound and unit transposons, integrons, and super integrons). An important class of intercellular MGE, the plasmids, act as transposon vectors and facilitate TE movement within the plasmidome.|alt=|border]] | ||
== Section Organization == | |||
'''This section encompasses several key topics:''' | |||
* '''[[General Information/Overview|Overview]]''': An introduction to the significance of TEs in bacterial genomes. | |||
* '''[[General Information/IS History|Insertion Sequence History and Early Transposition Models]]''': A historical perspective on the discovery and initial models explaining TE behavior. | |||
* '''[[General Information/What Is an IS?|What Is an IS?]]''': Detailed definitions and characteristics of insertion sequences. | |||
* '''[[General Information/ISfinder and the Growing Number of IS|ISfinder and the Growing Number of IS]]''': Insights into the expanding database of known insertion sequences. | |||
* '''[[General Information/IS Identification|IS Identification, Nomenclature, and Naming Attribution]]''': Guidelines on how insertion sequences are identified and named. | |||
* '''[[General Information/IS Distribution|IS Distribution]]''': Information on the prevalence and distribution patterns of insertion sequences across different bacterial species. | |||
* '''[[General Information/Major Groups are Defined by the Type of Transposase They Use|Major Groups Defined by the Type of Transposase They Use]]''': Classification of TEs based on the transposase enzymes they encode. | |||
* '''[[General Information/Fuzzy Borders|Fuzzy Borders]]''': Discussion on the complexities and ambiguities in defining the boundaries of TEs. | |||
* '''[[General Information/tIS - IS and relatives with passenger genes|tIS - IS and Relatives with Passenger Genes]]''': Examination of Insertion Sequences that carry additional genes, known as ''passenger genes''. | |||
* '''[[General Information/ IS derivatives of Tn3 family transposons|IS Derivatives of Tn''3'' Family Transposons]]''': Analysis of insertion sequences derived from Tn3 family transposons. | |||
* '''[[General Information/IS related to Integrative Conjugative Elements (ICEs)|IS Related to Integrative Conjugative Elements (ICEs)]]''': Exploration of the relationship between insertion sequences and ICEs. | |||
* '''[[General Information/IS91 and ISCR|IS''91'' and IS''CR'']]''': Specific focus on the IS''91'' family and IS''CR'' elements. | |||
* '''[[General Information/Non-autonomous IS derivatives|Non-autonomous IS Derivatives]]''': Study of insertion sequences that rely on other elements for mobility. | |||
* '''[[General Information/ Relationship Between IS and Eukaryotic TE|Relationship Between IS and Eukaryotic TE]]''': Comparative analysis of prokaryotic insertion sequences and eukaryotic transposable elements. | |||
* '''[[General Information/ Impact of IS on Genome Evolution - The Importance of Time Scale|Impact of IS on Genome Evolution - The Importance of Time Scale]]''': Insights into how insertion sequences influence genome evolution over time. | |||
* '''[[General Information/Target Choice|Target Choice]]''': Understanding the selection of insertion sites by TEs. | |||
* '''[[General Information/Influence of transposition mechanisms on genome impact|Influence of Transposition Mechanisms on Genome Impact]]''': Evaluation of how different transposition mechanisms affect genomic architecture. | |||
* '''[[General Information/IS and Gene Expression|IS and Gene Expression]]''': Investigation into how insertion sequences can modulate gene expression. | |||
* '''[[General Information/IS Organization|IS Organization]]''': Structural organization of insertion sequences within the genome. | |||
* '''[[General Information/Control of transposition activity|Control of Transposition Activity]]''': Mechanisms that regulate the activity of transposable elements. | |||
* '''[[General Information/Transposase expression and activity|Transposase Expression and Activity]]''': Details on the expression patterns and functionality of transposase enzymes. | |||
* '''[[General Information/Reaction mechanisms|Reaction Mechanisms]]''': Biochemical pathways facilitating transposition events. | |||
* '''[[General Information/The casposases|The Casposases]]''': Introduction to casposases and their role in the evolution of CRISPR-Cas systems. | |||
This section serves as a foundational resource for researchers and students aiming to understand the fundamental aspects of transposable elements before delving into specific families of insertion sequences and transposons detailed in other sections of TnPedia. | |||
== How to Cite? == | |||
TnPedia Team. (2025). TnPedia: General Information on Prokaryotic Elements. Zenodo. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.15548171 | |||
[[File:General_Info-badge.png|link=https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.15548171|DOI badge]] | |||
---- | |||
{{TnPedia}} | |||
<br | <br> | ||
{| style="width:340px; margin: 0 auto; background-color:#f0f0f0;" | |||
| {{#widget:ClustrMaps}} | |||
|} | |||
Latest revision as of 11:57, 1 June 2025
General Information on Prokaryotic Elements
The "General Information" section of TnPedia offers a comprehensive overview of prokaryotic transposable elements (TEs), which are central to bacterial evolution and adaptation. These mobile genetic elements facilitate the acquisition and dissemination of genes responsible for antibiotic resistance, heavy metal tolerance, and virulence factors.
| General Information on Prokaryotic Elements |
|
Section Organization
This section encompasses several key topics:
- Overview: An introduction to the significance of TEs in bacterial genomes.
- Insertion Sequence History and Early Transposition Models: A historical perspective on the discovery and initial models explaining TE behavior.
- What Is an IS?: Detailed definitions and characteristics of insertion sequences.
- ISfinder and the Growing Number of IS: Insights into the expanding database of known insertion sequences.
- IS Identification, Nomenclature, and Naming Attribution: Guidelines on how insertion sequences are identified and named.
- IS Distribution: Information on the prevalence and distribution patterns of insertion sequences across different bacterial species.
- Major Groups Defined by the Type of Transposase They Use: Classification of TEs based on the transposase enzymes they encode.
- Fuzzy Borders: Discussion on the complexities and ambiguities in defining the boundaries of TEs.
- tIS - IS and Relatives with Passenger Genes: Examination of Insertion Sequences that carry additional genes, known as passenger genes.
- IS Derivatives of Tn3 Family Transposons: Analysis of insertion sequences derived from Tn3 family transposons.
- IS Related to Integrative Conjugative Elements (ICEs): Exploration of the relationship between insertion sequences and ICEs.
- IS91 and ISCR: Specific focus on the IS91 family and ISCR elements.
- Non-autonomous IS Derivatives: Study of insertion sequences that rely on other elements for mobility.
- Relationship Between IS and Eukaryotic TE: Comparative analysis of prokaryotic insertion sequences and eukaryotic transposable elements.
- Impact of IS on Genome Evolution - The Importance of Time Scale: Insights into how insertion sequences influence genome evolution over time.
- Target Choice: Understanding the selection of insertion sites by TEs.
- Influence of Transposition Mechanisms on Genome Impact: Evaluation of how different transposition mechanisms affect genomic architecture.
- IS and Gene Expression: Investigation into how insertion sequences can modulate gene expression.
- IS Organization: Structural organization of insertion sequences within the genome.
- Control of Transposition Activity: Mechanisms that regulate the activity of transposable elements.
- Transposase Expression and Activity: Details on the expression patterns and functionality of transposase enzymes.
- Reaction Mechanisms: Biochemical pathways facilitating transposition events.
- The Casposases: Introduction to casposases and their role in the evolution of CRISPR-Cas systems.
This section serves as a foundational resource for researchers and students aiming to understand the fundamental aspects of transposable elements before delving into specific families of insertion sequences and transposons detailed in other sections of TnPedia.
How to Cite?
TnPedia Team. (2025). TnPedia: General Information on Prokaryotic Elements. Zenodo. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.15548171