IS Families: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (42 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[Image:1.6.1.png|thumb|520x520px|[[General Information/IS Distribution|'''Fig.1.6.1.''' IS distribution in the prokaryotic world.]] |alt= | == Introduction – Prokaryotic Insertion Sequences == | ||
Insertion sequences (IS) are the simplest, most abundant transposable elements found in bacteria and archaea. Since their discovery in the late 1960s, the catalogue of known IS has expanded explosively; today, '''[https://tncentral.ncc.unesp.br/ISfinder/index.php ISfinder]''' curates sequences for > 5,000 distinct elements drawn from nearly every branch of the prokaryotic tree. Far from genetic curiosities, IS act as powerful engines of genome evolution, capturing, shuffling, mutating, and occasionally activating host genes while driving plasmid and chromosomal rearrangements. Their activity underlies rapid adaptation to antibiotics, niche colonization, and metabolic innovation, making them indispensable subjects for comparative genomics and molecular microbiology.[[Image:1.6.1.png|thumb|520x520px|[[General Information/IS Distribution|'''Fig.1.6.1.''' IS distribution in the prokaryotic world.]] |alt=|link=https://tncentral.ncc.unesp.br/TnPedia/index.php/File:1.6.1.png]]Despite their sequence diversity, IS rely on a surprisingly small set of transposition chemistries—'''''cut-and-paste''''', '''''copy-out–paste-in''''', '''''peel-and-paste''''' and '''''rolling-circle''''' mechanisms chief among them. | |||
These shared strategies provide a conceptual framework for understanding how seemingly unrelated families achieve similar biological outcomes. They also blur the traditional borders between IS and larger composite transposons or integrative elements, emphasizing that mechanistic convergence, rather than sequence homology alone, now guides TE classification. | |||
== How to use this section == | |||
Each chapter that follows focuses on a single IS family. For every family you will find: | |||
* '''Diagnostic features''' – hallmark transposase motifs, terminal inverted repeats, and target-site duplications. | |||
* '''Mechanistic synopsis''' – the transposition pathway(s) employed and any known regulatory controls. | |||
* '''Representative members''' – well-characterized elements that exemplify the family’s diversity and biological impact. | |||
* '''Distribution and host range''' – taxonomic breadth and notable hotspots across plasmids, chromosomes, and mobile genomic islands. | |||
* '''Genomic and evolutionary impact''' – documented roles in gene mobilization, genome plasticity, and adaptive evolution. | |||
Because genome sequencing continues to reveal novel IS at an accelerating pace, family boundaries and definitions remain fluid. These chapters therefore serve not as static taxonomic verdicts but as living reference points that will be updated as new data emerge. | |||
Whether you are annotating a newly sequenced genome, tracking the spread of antibiotic-resistance genes, or probing the evolutionary logic of mobile DNA, this section of '''TnPedia''' provides a concise, family-by-family guide to the structure, mechanism, and biological significance of prokaryotic insertion sequences. | |||
{| class="wikitable" | |||
!Prokaryotic [[IS Families|Insertion Sequences]] Families | |||
|- | |||
|'''1. [[IS Families/IS1 family|IS<i>1</i> family]]''' | |||
|- | |||
|'''2. [[IS Families/IS1595 family|IS<i>1595</i> family]]''' | |||
|- | |||
|'''3. [[IS Families/IS3 family|IS<i>3</i> family]]''' | |||
'''3a. [[IS Families/IS3_family#Excision:_A_dedicated_enzyme|Excision: A dedicated enzyme]]''' | |||
|- | |||
|'''4. [[IS Families/IS481 family|IS<i>481</i> family]]''' | |||
|- | |||
|'''5. [[IS Families/IS1202 family|IS''1202'' family]]''' | |||
|- | |||
|'''6. [[IS Families/IS4 and related families|IS<i>4</i> and related families]]: [[IS Families/IS4 and related families#IS701 family|IS<i>701</i> family]], [[IS Families/IS4 and related families#ISH3 family|IS''H3'' family]] and [[IS Families/IS4 and related families#IS1634 family|IS''1634'' family]]''' | |||
|- | |||
|'''7. [[IS Families/IS5 and related IS1182 families|IS<i>5</i> and related IS<i>1182</i> families]]''' | |||
|- | |||
|'''8. [[IS Families/IS6 family|IS<i>6</i> family]]''' | |||
|- | |||
|'''9. [[IS Families/IS21 family|IS<i>21</i> family]]''' | |||
|- | |||
|'''10. [[IS Families/IS30 family|IS<i>30</i> family]]''' | |||
|- | |||
|'''11. [[IS Families/IS66 family|IS<i>66</i> family]]''' | |||
|- | |||
|'''12. [[IS Families/IS110 family|IS<i>110</i> and IS''1111'' families]]''' | |||
|- | |||
|'''13. [[IS Families/IS256 family|IS<i>256</i> family]]''' | |||
|- | |||
|'''14. [[IS Families/IS630 family|IS<i>630</i> family]]''' | |||
|- | |||
|'''15. [[IS Families/IS982 family|IS<i>982</i> family]]''' | |||
|- | |||
|'''16. [[IS Families/IS1380 family|IS<i>1380</i> family]]''' | |||
|- | |||
|'''17. [[IS Families/ISAs1 family|IS<i>As1</i> family]]''' | |||
|- | |||
|'''18. [[IS Families/ISL3 family|IS''L3'' family]]''' | |||
|- | |||
|'''19. [[IS Families/ISAzo13 family|IS<i>Azo13</i> family]]''' | |||
|- | |||
|'''20. [[IS Families/IS607 family|IS''607'' family]]''' | |||
|- | |||
|'''21. [[IS Families/IS91-ISCR families|IS''91'' and related IS''CR'' families]]''' | |||
|- | |||
|'''22. [[IS Families/IS200-IS605 family|IS<i>200</i>/IS<i>605</i> family]]''' | |||
|- | |||
|'''23. [[IS Families/ISPa17 family|IS<i>Pa17</i> family]]''' | |||
|} | |} | ||
== Quick Access Table == | |||
'''Main Characteristics and Summary of Each IS family and Sub-Groups''' | |||
Below is a concise summary table of key characteristics for each IS family and their subgroups, including conserved transposase motifs, transposition mechanisms, typical size, hallmark IRs/DRs sequences. Use this as a practical reference guide to quickly locate essential information before diving into individual family chapters. | |||
{| class="wikitable" style="margin:auto" | {| class="wikitable" style="margin:auto" | ||
| colspan="10" |'''Characteristics of insertion sequence families. Abbreviations: DR, duplication repeat; IS, insertion sequence; ORF, open reading frame.''' | | colspan="10" |'''Characteristics of insertion sequence families. Abbreviations: DR, duplication repeat; IS, insertion sequence; ORF, open reading frame.''' | ||
| Line 115: | Line 128: | ||
|DDE | |DDE | ||
|copy-and-paste (?) | |copy-and-paste (?) | ||
|- | |||
| rowspan="3" |[[IS Families/IS1202 family|IS<i>1202</i>]] | |||
|[https://tncentral.ncc.unesp.br/ISfinder/scripts/ficheIS.php?name=ISAba32 IS''Aba32''] | |||
|1450-1870 | |||
|5-6 | |||
|TGT | |||
| rowspan="3" |Y | |||
| rowspan="3" |1 | |||
| rowspan="3" |— | |||
| rowspan="3" |DDE | |||
| rowspan="3" |copy-and-paste | |||
|- | |||
|[https://tncentral.ncc.unesp.br/ISfinder/scripts/ficheIS.php?name=ISTde1 IS''Tde1''] | |||
|1320-1780 | |||
|16-17 | |||
|TAT/TGT | |||
|- | |||
|[https://tncentral.ncc.unesp.br/ISfinder/scripts/ficheIS.php?name=IS1202 IS''1202''] | |||
|1440-1900 | |||
|27-28 | |||
|TGT | |||
|- | |- | ||
| rowspan="7" |[[IS Families/IS4 and related families|IS<i>4</i>]] | | rowspan="7" |[[IS Families/IS4 and related families|IS<i>4</i>]] | ||
| Line 212: | Line 246: | ||
|[[IS Families/IS607 family|IS<i>607</i>]]||—||1700–2500||0||—||N||2*||—||Serine**||— | |[[IS Families/IS607 family|IS<i>607</i>]]||—||1700–2500||0||—||N||2*||—||Serine**||— | ||
|- | |- | ||
|[[IS Families/ | |[[IS Families/ISPa17 family|IS''Pa17'']] | ||
| | |— | ||
| | |2000-2500 | ||
|5 | |5 | ||
| | |— | ||
|Y | |Y | ||
| | |4+pass | ||
|— | |||
|— | |— | ||
|— | |— | ||
|- | |- | ||
| rowspan="8" |IS<i>NCY '''*'''</i> | | rowspan="8" |[[ISNYC|IS<i>NCY</i>]] <i>'''*'''</i> | ||
|IS<i>892</i>||1600||0–8||CTAG||Y||2|| rowspan="7" |ORFAB|| rowspan="7" |—|| rowspan="7" |— | |IS<i>892</i>||1600||0–8||CTAG||Y||2|| rowspan="7" |ORFAB|| rowspan="7" |—|| rowspan="7" |— | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 248: | Line 282: | ||
|— | |— | ||
|}<center>'''*''' IS''NCY ='' '''I'''nsertion '''S'''equence '''N'''ot '''C'''lassified '''Y'''et</center><br /> | |}<center>'''*''' IS''NCY ='' '''I'''nsertion '''S'''equence '''N'''ot '''C'''lassified '''Y'''et</center><br /> | ||
< | <br/> | ||
<br/> | |||
<br /> | |||
{{TnPedia}} | {{TnPedia}} | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
{| style="width:340px; margin: 0 auto; background-color:#f0f0f0;" | |||
| {{#widget:ClustrMaps}} | |||
|} | |||
Latest revision as of 13:32, 10 June 2025
Introduction – Prokaryotic Insertion Sequences
Insertion sequences (IS) are the simplest, most abundant transposable elements found in bacteria and archaea. Since their discovery in the late 1960s, the catalogue of known IS has expanded explosively; today, ISfinder curates sequences for > 5,000 distinct elements drawn from nearly every branch of the prokaryotic tree. Far from genetic curiosities, IS act as powerful engines of genome evolution, capturing, shuffling, mutating, and occasionally activating host genes while driving plasmid and chromosomal rearrangements. Their activity underlies rapid adaptation to antibiotics, niche colonization, and metabolic innovation, making them indispensable subjects for comparative genomics and molecular microbiology.
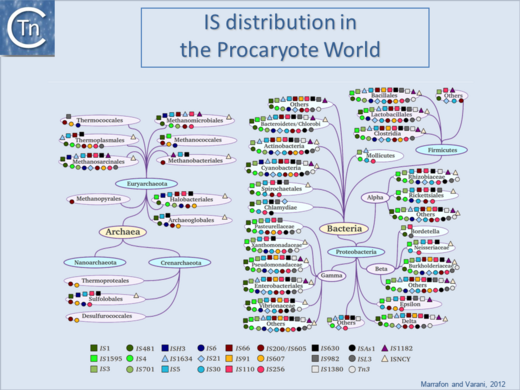
Despite their sequence diversity, IS rely on a surprisingly small set of transposition chemistries—cut-and-paste, copy-out–paste-in, peel-and-paste and rolling-circle mechanisms chief among them.
These shared strategies provide a conceptual framework for understanding how seemingly unrelated families achieve similar biological outcomes. They also blur the traditional borders between IS and larger composite transposons or integrative elements, emphasizing that mechanistic convergence, rather than sequence homology alone, now guides TE classification.
How to use this section
Each chapter that follows focuses on a single IS family. For every family you will find:
- Diagnostic features – hallmark transposase motifs, terminal inverted repeats, and target-site duplications.
- Mechanistic synopsis – the transposition pathway(s) employed and any known regulatory controls.
- Representative members – well-characterized elements that exemplify the family’s diversity and biological impact.
- Distribution and host range – taxonomic breadth and notable hotspots across plasmids, chromosomes, and mobile genomic islands.
- Genomic and evolutionary impact – documented roles in gene mobilization, genome plasticity, and adaptive evolution.
Because genome sequencing continues to reveal novel IS at an accelerating pace, family boundaries and definitions remain fluid. These chapters therefore serve not as static taxonomic verdicts but as living reference points that will be updated as new data emerge.
Whether you are annotating a newly sequenced genome, tracking the spread of antibiotic-resistance genes, or probing the evolutionary logic of mobile DNA, this section of TnPedia provides a concise, family-by-family guide to the structure, mechanism, and biological significance of prokaryotic insertion sequences.
| Prokaryotic Insertion Sequences Families |
|---|
| 1. IS1 family |
| 2. IS1595 family |
| 3. IS3 family |
| 4. IS481 family |
| 5. IS1202 family |
| 6. IS4 and related families: IS701 family, ISH3 family and IS1634 family |
| 7. IS5 and related IS1182 families |
| 8. IS6 family |
| 9. IS21 family |
| 10. IS30 family |
| 11. IS66 family |
| 12. IS110 and IS1111 families |
| 13. IS256 family |
| 14. IS630 family |
| 15. IS982 family |
| 16. IS1380 family |
| 17. ISAs1 family |
| 18. ISL3 family |
| 19. ISAzo13 family |
| 20. IS607 family |
| 21. IS91 and related ISCR families |
| 22. IS200/IS605 family |
| 23. ISPa17 family |
Quick Access Table
Main Characteristics and Summary of Each IS family and Sub-Groups
Below is a concise summary table of key characteristics for each IS family and their subgroups, including conserved transposase motifs, transposition mechanisms, typical size, hallmark IRs/DRs sequences. Use this as a practical reference guide to quickly locate essential information before diving into individual family chapters.
| Characteristics of insertion sequence families. Abbreviations: DR, duplication repeat; IS, insertion sequence; ORF, open reading frame. | |||||||||
| Families | Sub-Groups | Typical size-range (bp) | DR (bp) | Ends | IRs | No ORFs | Frameshift | Catalytic residues | Mechanism |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IS1 | — | 740–1180 | 8–9 | GGnnnTG | Y | 2 | ORFAB | DDE | copy-and-paste and cointegrate |
| single ORF | 800–1200 | 0–9 | N | 1 | — | ||||
| ISMhu11 | 900–4600 | 0–10 | Y | 2 | ORFAB | ||||
| IS1595 | ISPna2 | 1000–1150 | 8 | GGCnnTG | Y | 1 | — | DDNK | copy-and-paste (?) |
| ISPna2+pass | 1500–2600 | 8 | — | 1+pass | — | ||||
| ISH4 | 1000 | 8 | CGCTCTT | 1 | DDNK | ||||
| IS1016 | 700–745 | 7–9 | GGGgctg | DDEK | |||||
| IS1595 | 900–1100 | 8 | CcTGATT | DDNK+ER4R7 | |||||
| ISSod11 | 1000–1100 | 8 | nnnGcnTATC | DDHK+ER4R7 | |||||
| ISNwi1 | 1080–1200 | 8 | ggnnatTAT | DDEK+ER4 | |||||
| ISNwi1+pass | 1750–4750 | 8 | — | 1+pass | — | ||||
| ISNha5 | 3450–7900 | 8 | CGGnnTT | 1 | DDER/K | ||||
| IS3 | IS150 | 1200–1600 | 3–4 | TG | Y | 2 | ORFAB | DDE | copy-and-paste |
| IS407 | 1100–1400 | 4 | TG | ||||||
| IS51 | 1000–1400 | 3–4 | TG | ||||||
| IS3 | 1150–1750 | 3–4 | TGa/g | ||||||
| IS2 | 1300–1400 | 5 | TG | ||||||
| IS481 | — | 950–1300 | 4–15 | TGT | Y | 1 | — | DDE | copy-and-paste (?) |
| IS1202 | ISAba32 | 1450-1870 | 5-6 | TGT | Y | 1 | — | DDE | copy-and-paste |
| ISTde1 | 1320-1780 | 16-17 | TAT/TGT | ||||||
| IS1202 | 1440-1900 | 27-28 | TGT | ||||||
| IS4 | IS10 | 1200–1350 | 9 | CT | Y | 1 | DDE | hairpin intermediate | cut-and-paste |
| IS50 | 1350–1550 | 8–9 | C | hairpin intermediate | |||||
| ISPepr1 | 1500–1600 | 7–8 | -T-AA | ? | |||||
| IS4 | 1400–1600 | 10–13 | -AAT | ? | |||||
| IS4Sa | 1150–1750 | 8–10 | CA | ? | |||||
| ISH8 | 1400–1800 | 10 | ? | ||||||
| IS231 | 1450–5400 | 10–12 | CAT | 1 or + * | *passenger genes | ||||
| IS701 | — | 1400–1550 | 4 | — | Y | 1 | — | DDE | — |
| ISAba11 | — | — | |||||||
| ISH3 | — | 1225–1500 | 4–5 | C-GT | Y | 1 | — | DDE | — |
| IS1634 | — | 1500–2000 | 5–6 | C | Y | 1 | — | DDE | — |
| IS5 | IS903 | 950–1150 | 9 | GG | Y | 1 | — | DDE | — |
| ISL2 | 850–1200 | 2–3 | — | ||||||
| ISH1 | 900–1150 | 8 | -GC | ||||||
| IS5 | 1000–1500 | 4 | Ga/g | ||||||
| IS1031 | 850–1050 | 3 | GAa/g | ||||||
| IS427 | 800–1000 | 2–4 | Ga/g | 2 | ORFAB | ||||
| IS1182 | — | 1330–1950 | 0–60 | — | Y | 1 | — | DDE | — |
| IS6 | — | 700–900 | 8 | GG | Y | 1 | — | DDE | co-integrate |
| IS21 | — | 1750–2600 | 4–8 | TG | Y | 2 * | — | DDE | — |
| IS30 | — | 1000–1700 | 2–3 | — | Y | 1 | — | DDE | copy-and-paste |
| IS66 | — | 2000–3000 | 8–9 | GTAA | Y | 3* | — | DDE* | — |
| ISBst12 | 1350–1900 | 1 | DDE | ||||||
| IS256 | — | 1200–1500 | 8–9 | Ga/g | Y | 1 | — | DDE | copy-and-paste |
| IS1249 | 1300 | 0–10 | GG | ||||||
| ISC1250 | 1250 | 0–9 | GG | ||||||
| ISH6 | — | 1450 | 8 | GGT | Y | 1 | — | DDE | — |
| ISLre2 | — | 1500–2000 | 9 | — | Y | 1 | — | DDE | — |
| ISKra4 | ISAzba1 | 1400–2900 | 0 | — | Y | 1 or + * | — | DDE | — |
| ISMich2 | 1250–1400 | 8 | GGG | 1 or 2 | ORFAB | ||||
| ISKra4 | 1400–3700 | 9 | GGG | 1 or + * | — | ||||
| IS630 | — | 1000–1400 | 2* | — | Y | 1 or 2 | ORFAB | DDE | cut-and-paste |
| IS982 | — | 1000 | 3–9 | AC | Y | 1 | — | DDE | — |
| IS1380 | — | 1550–2000 | 4–5 | CC | Y | 1 | — | DDE | — |
| ISAs1 | — | 1200–1500 | 8–10 | CAGGG | Y | 1 | — | — | — |
| ISL3 | — | 1300–2300 | 8 | GG | Y | 1 | — | — | — |
| Tn3 | — | >3000 | 0 | GGGG | Y | >1 | — | DDE | co-integrate |
| ISAzo13 | — | 1250–2200 | 0–4 | Ga/g | Y | 1 | — | — | — |
| IS110 | — | 1200–1550 | 0 | — | N | 1 | — | DEDD | — |
| IS1111 | — | — | — | Y* | — | — | — | — | |
| IS91 | — | 1500–2000 | 0 | — | N | 1 | — | HUH/Y2 | rolling-circle |
| IS200/IS605 | IS200 | 600–750 | 0 | — | 0 | 1* | — | HUH/Y1 | peel-and-paste |
| IS605 | 1300–2000 | — | — | — | 2* | — | HUH/Y1** | ||
| IS607 | — | 1700–2500 | 0 | — | N | 2* | — | Serine** | — |
| ISPa17 | — | 2000-2500 | 5 | — | Y | 4+pass | — | — | — |
| ISNCY * | IS892 | 1600 | 0–8 | CTAG | Y | 2 | ORFAB | — | — |
| ISLbi1 | 1400–1500 | 5 | — | Y | 1 | ||||
| ISMae2 | 1400–2400 | 9 | CAG | Y | 1 | ||||
| ISPlu15 | 800–1000 | 0 | — | N | 1 | ||||
| ISA1214 | 1000–1200 | 8–12 | — | Y | 2 | ||||
| ISC1217 | 1200 | 6–8 | TAG | Y | 1 | ||||
| ISM1 | 1300–1600 | 8–9 | — | Y | 1 | ||||
| ISDol1 | 1600–1900 | 6–7 | — | Y | 1 | — | DDE | — | |