General Information/The casposases: Difference between revisions
m Text replacement - "{{#" to "{{#pmid:" |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
==Bibliography== | ==Bibliography== | ||
{{Reflist|32em}} | {{Reflist|32em}} | ||
<hr> | == How to Cite? == | ||
TnPedia Team. (2025). TnPedia: General Information on Prokaryotic Elements. Zenodo. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.15548171 | |||
[[File:General_Info-badge.png|link=https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.15548171|DOI badge]]<hr> | |||
{{TnPedia}} | {{TnPedia}} | ||
Latest revision as of 18:20, 29 May 2025
The casposases
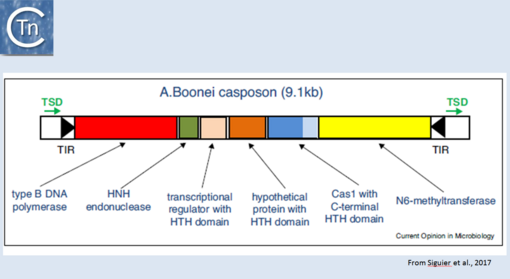
More recently, TE related to CRISPRs, Casposons have been identified[1] and a reassement of their ends has led to the identification of an 14-15 bp target duplication [2]. Moreover, the purified Cas1 enzyme encoded by these ancestral transposons has been demonstrated to catalyse strand transfer of a pre-cleaved transposon in vitro but does not appear to promote transposon strand cleavage in this assay[3]. Cas1 "casposases" use similar chemistry to that used by the CRISPR Cas1-Cas2 complex but with opposite substrate specificities since CRISPR Cas1-Cas2 integrates "random" sequences into a specific site in the CRISPR locus whereas casposases integrate a specific site (the casposon ends) into random target sequences (Fig.24.1).
Bibliography
- ↑ Krupovic et al.. Casposons: a new superfamily of self-synthesizing DNA transposons at the origin of prokaryotic CRISPR-Cas immunity. BMC biology. 2014. 12. pp. 36. doi: 10.1186/1741-7007-12-36. PMID: 24884953.
- ↑ Hickman & Dyda. CRISPR-Cas immunity and mobile DNA: a new superfamily of DNA transposons encoding a Cas1 endonuclease. Mobile DNA. 2014. 5. pp. 23. doi: 10.1186/1759-8753-5-23. PMID: 25180049.
- ↑ Hickman & Dyda. The casposon-encoded Cas1 protein from Aciduliprofundum boonei is a DNA integrase that generates target site duplications. Nucleic acids research. 2015. 43. pp. 10576-87. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv1180. PMID: 26573596.
How to Cite?
TnPedia Team. (2025). TnPedia: General Information on Prokaryotic Elements. Zenodo. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.15548171